3. Polygon construction
developing an algorithm for an animation of a geometric construction, or a visual proof, evaluating the algorithm using test cases
3.1. Equilateral triangle
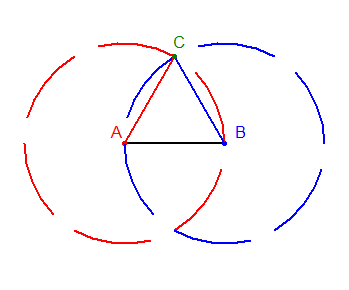
Input: a line segment AB with length L
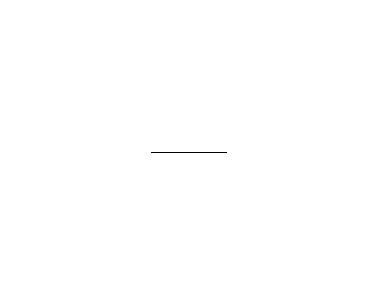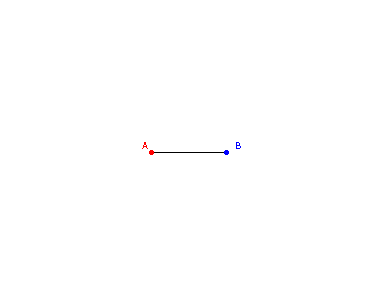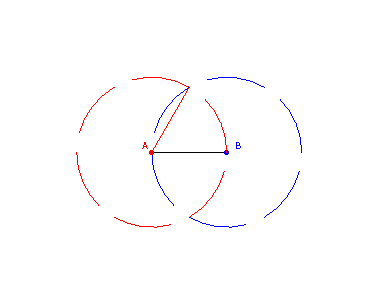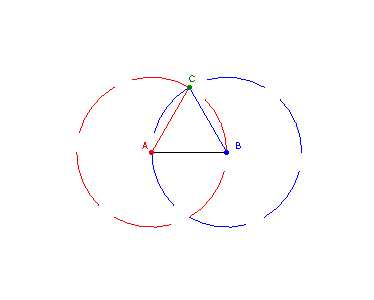
Step 1: Draw a circle C1 with center A and radius L
Step 2: Draw a circle C2 with center B and radius L
Step 3: Find the point C where C1 and C2 intersect
Step 4: Draw a line segment AC
Step 5: Draw a line segment BC
Step 6: Triangle ABC is equilateral with side length L
1import turtle
2import math
3
4
5def label_point(t, label, deltax=-12, deltay=2, penc="black"):
6 """
7 Write a label next to the current position of the turtle.
8
9 Args:
10 t (turtle.Turtle): The turtle object used for drawing.
11 label (str): The text to be displayed as the label.
12 deltax (int, optional): The horizontal offset from the turtle's position. Defaults to -12.
13 deltay (int, optional): The vertical offset from the turtle's position. Defaults to 2.
14 penc (str, optional): The color of the text. Defaults to "black".
15 """
16 t.penup() # Lift the pen to avoid drawing while moving
17 t.setx(t.xcor() + deltax) # Move the turtle horizontally by deltax units
18 t.sety(t.ycor() + deltay) # Move the turtle vertically by deltay units
19 t.pendown() # Lower the pen to start drawing
20 t.pencolor(penc) # Set the pen color for the label
21 t.write(label, font=("Arial", 12, "normal")) # Display the label using the specified font
22
23
24def move_to(t, point):
25 """
26 Move the turtle to a specified point without drawing.
27
28 Args:
29 t (turtle.Turtle): The turtle object used for drawing.
30 point (tuple): The coordinates of the target point (x, y).
31 """
32 t.penup() # Lift the pen to avoid drawing while moving
33 t.goto(point) # Move the turtle to the specified point
34
35
36def move_arc(t, centre=(0, 0), angle=0, radius=10, extent=360):
37 """
38 Move the turtle along an arc with a given center, angle, radius, and extent.
39
40 Args:
41 t (turtle.Turtle): The turtle object used for drawing.
42 centre (tuple, optional): The coordinates of the center of the arc (x, y). Defaults to (0, 0).
43 angle (int, optional): The angle of the initial position of the turtle relative to the center. Defaults to 0.
44 radius (int, optional): The radius of the arc. Defaults to 10.
45 extent (int, optional): The angle of the arc that the turtle moves along. Defaults to 360.
46 """
47 move_to(t, centre) # Move the turtle to the specified center
48 t.seth(angle) # Set the turtle's heading (angle) to the initial angle
49 t.fd(radius) # Move the turtle forward by the specified radius
50 t.seth(angle + 90) # Set the turtle's heading to be perpendicular to the initial angle
51 t.circle(radius, extent=extent) # Draw an arc with the specified radius and extent
52
53
54def draw_line_points(t, point1, point2, penw=1, penc="black"):
55 """
56 Draw a straight line from a starting point (point1) to an ending point (point2) using the specified pen width and color.
57
58 Args:
59 t (turtle.Turtle): The turtle object used for drawing.
60 point1 (tuple): The coordinates of the starting point (x, y).
61 point2 (tuple): The coordinates of the ending point (x, y).
62 penw (int, optional): The width of the line. Defaults to 1.
63 penc (str, optional): The color of the line. Defaults to "black".
64 """
65 move_to(t, point1) # Move the turtle to the starting point
66 t.pendown() # Put the pen down to start drawing
67 t.pencolor(penc) # Set the pen color
68 t.pensize(penw) # Set the pen width
69 t.goto(point2) # Draw a straight line to the ending point
70
71
72def draw_centered_arc(t, centre=(0, 0), angle=0, radius=10, extent=360, penw=1, penc="black"):
73 """
74 Draw an arc with a given center, angle, radius, extent, pen width, and color.
75
76 Args:
77 t (turtle.Turtle): The turtle object used for drawing.
78 centre (tuple, optional): The coordinates of the center of the arc (x, y). Defaults to (0, 0).
79 angle (int, optional): The angle of the initial position of the turtle relative to the center. Defaults to 0.
80 radius (int, optional): The radius of the arc. Defaults to 10.
81 extent (int, optional): The angle of the arc that the turtle draws. Defaults to 360.
82 penw (int, optional): The width of the pen. Defaults to 1.
83 penc (str, optional): The color of the pen. Defaults to "black".
84 """
85 move_to(t, centre) # Move the turtle to the specified center
86 t.seth(angle) # Set the turtle's heading (angle) to the initial angle
87 t.pensize(penw) # Set the pen width
88 t.pencolor(penc) # Set the pen color
89 t.fd(radius) # Move the turtle forward by the specified radius
90 t.pd() # Put the pen down to start drawing
91 t.seth(angle + 90) # Set the turtle's heading to be perpendicular to the initial angle
92 t.circle(radius, extent=extent) # Draw an arc with the specified radius and extent
93
94 # Draw dots at regular intervals along the arc
95 for i in range(int((360 - extent) / 60)):
96 t.pd() # Put the pen down to draw
97 t.circle(radius, extent=45) # Draw a small arc segment
98 t.pu() # Lift the pen to stop drawing
99 t.circle(radius, extent=15) # Move to the next position to draw a dot
100
101
102def construct_equilateral_triangle(t, L, w):
103 # Hide the turtle
104 t.hideturtle()
105 A = (-L / 2, 0)
106 B = (L / 2, 0)
107 C = (0, L * math.sqrt(3) / 2)
108 # Draw the line segment AB
109 draw_line_points(t, A, B, penw=w, penc="black")
110
111 # Label the point A
112 move_to(t, (-L / 2, 0))
113 t.dot(5, "red")
114 label_point(t, "A", deltax=-12, deltay=2, penc="red")
115
116 # Label the point B
117 move_to(t, (L / 2, 0))
118 t.dot(5, "blue")
119 label_point(t, "B", deltax=12, deltay=2, penc="blue")
120
121 # Draw the circle C1 with center A and radius L
122 draw_centered_arc(t, (-L / 2, 0), angle=0, radius=L, extent=0, penw=w, penc="red")
123 # Draw the circle C2 with center B and radius L
124 draw_centered_arc(t, (L / 2, 0), angle=120, radius=L, extent=0, penw=w, penc="blue")
125 # Draw the line segment AC
126 draw_line_points(t, A, C, penw=w, penc="red")
127 # Draw the line segment BC
128 draw_line_points(t, B, C, penw=w, penc="blue")
129 # Label the point C
130 t.dot(5, "green")
131 label_point(t, "C", deltax=0, deltay=5, penc="green")
132
133
134
135def main():
136 SCREEN_WIDTH = 800
137 SCREEN_HEIGHT = 600
138 L = 100
139
140 # Set up the turtle screen
141 s = turtle.Screen()
142 s.bgcolor("white")
143 s.title("equilateral triangle construction")
144 s.setup(width=SCREEN_WIDTH, height=SCREEN_HEIGHT, startx=0, starty=0)
145 s.tracer(1, 10)
146
147 # Create a turtle object
148 t = turtle.Turtle()
149 t.speed(10) # Set the turtle's speed to the fastest
150 t.ht()
151
152
153 # Call the function to construct the triangle
154 construct_equilateral_triangle(t, L, 1)
155
156 s.update()
157 s.exitonclick()
158
159
160if __name__ == "__main__":
161 main()
1import turtle
2import math
3import io
4from PIL import Image
5from pathlib import Path
6
7
8
9currfile_dir_dir = Path(__file__).parent.parent # Get the directory of the current script
10
11
12def label_point(t, label, deltax=-12, deltay=2, penc="black"):
13 """
14 Write a label next to the current position of the turtle.
15
16 Args:
17 t (turtle.Turtle): The turtle object used for drawing.
18 label (str): The text to be displayed as the label.
19 deltax (int, optional): The horizontal offset from the turtle's position. Defaults to -12.
20 deltay (int, optional): The vertical offset from the turtle's position. Defaults to 2.
21 penc (str, optional): The color of the text. Defaults to "black".
22 """
23 t.penup() # Lift the pen to avoid drawing while moving
24 t.setx(t.xcor() + deltax) # Move the turtle horizontally by deltax units
25 t.sety(t.ycor() + deltay) # Move the turtle vertically by deltay units
26 t.pendown() # Lower the pen to start drawing
27 t.pencolor(penc) # Set the pen color for the label
28 t.write(label, font=("Arial", 12, "normal")) # Display the label using the specified font
29
30
31
32def move_to(t, point):
33 """
34 Move the turtle to a specified point without drawing.
35
36 Args:
37 t (turtle.Turtle): The turtle object used for drawing.
38 point (tuple): The coordinates of the target point (x, y).
39 """
40 t.penup() # Lift the pen to avoid drawing while moving
41 t.goto(point) # Move the turtle to the specified point
42
43
44def move_arc(t, centre=(0, 0), angle=0, radius=10, extent=360):
45 """
46 Move the turtle along an arc with a given center, angle, radius, and extent.
47
48 Args:
49 t (turtle.Turtle): The turtle object used for drawing.
50 centre (tuple, optional): The coordinates of the center of the arc (x, y). Defaults to (0, 0).
51 angle (int, optional): The angle of the initial position of the turtle relative to the center. Defaults to 0.
52 radius (int, optional): The radius of the arc. Defaults to 10.
53 extent (int, optional): The angle of the arc that the turtle moves along. Defaults to 360.
54 """
55 move_to(t, centre) # Move the turtle to the specified center
56 t.seth(angle) # Set the turtle's heading (angle) to the initial angle
57 t.fd(radius) # Move the turtle forward by the specified radius
58 t.seth(angle + 90) # Set the turtle's heading to be perpendicular to the initial angle
59 t.circle(radius, extent=extent) # Draw an arc with the specified radius and extent
60
61
62def draw_line_points(t, point1, point2, penw=1, penc="black"):
63 """
64 Draw a straight line from a starting point (point1) to an ending point (point2) using the specified pen width and color.
65
66 Args:
67 t (turtle.Turtle): The turtle object used for drawing.
68 point1 (tuple): The coordinates of the starting point (x, y).
69 point2 (tuple): The coordinates of the ending point (x, y).
70 penw (int, optional): The width of the line. Defaults to 1.
71 penc (str, optional): The color of the line. Defaults to "black".
72 """
73 move_to(t, point1) # Move the turtle to the starting point
74 t.pendown() # Put the pen down to start drawing
75 t.pencolor(penc) # Set the pen color
76 t.pensize(penw) # Set the pen width
77 t.goto(point2) # Draw a straight line to the ending point
78
79
80def draw_centered_arc(t, centre=(0, 0), angle=0, radius=10, extent=360, penw=1, penc="black"):
81 """
82 Draw an arc with a given center, angle, radius, extent, pen width, and color.
83
84 Args:
85 t (turtle.Turtle): The turtle object used for drawing.
86 centre (tuple, optional): The coordinates of the center of the arc (x, y). Defaults to (0, 0).
87 angle (int, optional): The angle of the initial position of the turtle relative to the center. Defaults to 0.
88 radius (int, optional): The radius of the arc. Defaults to 10.
89 extent (int, optional): The angle of the arc that the turtle draws. Defaults to 360.
90 penw (int, optional): The width of the pen. Defaults to 1.
91 penc (str, optional): The color of the pen. Defaults to "black".
92 """
93 move_to(t, centre) # Move the turtle to the specified center
94 t.seth(angle) # Set the turtle's heading (angle) to the initial angle
95 t.pensize(penw) # Set the pen width
96 t.pencolor(penc) # Set the pen color
97 t.fd(radius) # Move the turtle forward by the specified radius
98 t.pd() # Put the pen down to start drawing
99 t.seth(angle + 90) # Set the turtle's heading to be perpendicular to the initial angle
100 t.circle(radius, extent=extent) # Draw an arc with the specified radius and extent
101
102 # Draw dots at regular intervals along the arc
103 for i in range(int((360 - extent) / 60)):
104 t.pd() # Put the pen down to draw
105 t.circle(radius, extent=45) # Draw a small arc segment
106 t.pu() # Lift the pen to stop drawing
107 t.circle(radius, extent=15) # Move to the next position to draw a dot
108
109
110# Define a function to construct an equilateral triangle
111def construct_equilateral_triangle_step(t, L, w, frame):
112 # Hide the turtle
113 t.hideturtle()
114 A = (-L / 2, 0)
115 B = (L / 2, 0)
116 C = (0, L * math.sqrt(3) / 2)
117
118 if frame == 0:
119 # Draw the line segment AB
120 draw_line_points(t, A, B, penw=w, penc="black")
121 elif frame == 1:
122 # Label the point A
123 move_to(t, A)
124 t.dot(5, "red")
125 label_point(t, "A", deltax=-12, deltay=2, penc="red")
126 elif frame == 2:
127 # Label the point B
128 move_to(t, B)
129 t.dot(5, "blue")
130 label_point(t, "B", deltax=12, deltay=2, penc="blue")
131 elif frame == 3:
132 # Draw the circle C1 with center A and radius L
133 draw_centered_arc(t, A, angle=0, radius=L, extent=0, penw=w, penc="red")
134 elif frame == 4:
135 # Draw the circle C2 with center B and radius L
136 draw_centered_arc(t, B, angle=120, radius=L, extent=0, penw=w, penc="blue")
137 # Find the point C where C1 and C2 intersect
138 # This can be done by using some trigonometry
139 # The angle between AB and AC is 60 degrees
140 # The distance from A to C is L
141 # The x-coordinate of C is L * cos(60) = L/2
142 # The y-coordinate of C is L * sin(60) = L * sqrt(3) / 2
143 elif frame == 5:
144 # Draw the line segment AC
145 draw_line_points(t, A, C, penw=w, penc="red")
146 elif frame == 6:
147 # Draw the line segment BC
148 draw_line_points(t, B, C, penw=w, penc="blue")
149 # Label the point C
150 elif frame == 7:
151 t.dot(5, "green")
152 label_point(t, "C", deltax=0, deltay=5, penc="green")
153
154
155def wait_for_click(x, y):
156 """
157 Callback function to wait for a mouse click event.
158
159 Args:
160 x (float): The x-coordinate of the mouse click.
161 y (float): The y-coordinate of the mouse click.
162 """
163 global continue_animation
164 continue_animation = True
165
166
167def main():
168 """
169 Main function to create an animated GIF of the step-by-step construction of an equilateral triangle.
170
171 Note:
172 This function sets up the turtle screen, waits for a mouse click to proceed to the next step,
173 calls the `construct_equilateral_triangle_step` function to construct each step of the triangle,
174 captures each frame as an image, and then saves the frames as an animated GIF.
175 """
176 global continue_animation
177 SCREEN_WIDTH = 500
178 SCREEN_HEIGHT = 400
179 L = 100
180 # Set up the turtle screen
181 s = turtle.Screen()
182 s.bgcolor("white")
183 s.title("Equilateral Triangle Construction")
184 s.setup(width=SCREEN_WIDTH, height=SCREEN_HEIGHT, startx=0, starty=0)
185 s.tracer(1, 10)
186 # Create a turtle object
187 t = turtle.Turtle()
188 t.speed(10)
189 t.ht()
190 images = [] # List to hold frames for the GIF
191 # Wait for a mouse click before proceeding to the next step
192 s.update()
193 continue_animation = False
194 while not continue_animation:
195 s.onclick(wait_for_click)
196 s.update()
197 # Call the function to construct each step of the triangle
198 for step in range(8):
199 construct_equilateral_triangle_step(t, L, 1, step)
200 # Capture the screen as an image and append it to the list
201 screen_img = s.getcanvas().postscript(colormode="color")
202 img = Image.open(io.BytesIO(screen_img.encode("utf-8")))
203 images.append(img)
204 # Define the path for the GIF
205 gif_path = currfile_dir_dir / "gifs" / "construct_equilateral_triangle.gif"
206 # Save the frames as a GIF
207 images[0].save(gif_path, save_all=True, append_images=images[1:], duration=8000 / 8, loop=0, dpi=600)
208 s.bye()
209
210
211if __name__ == "__main__":
212 main()
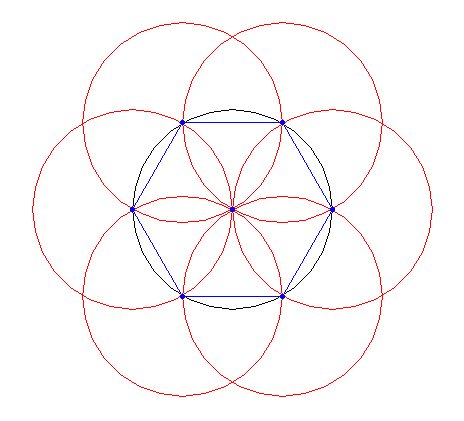
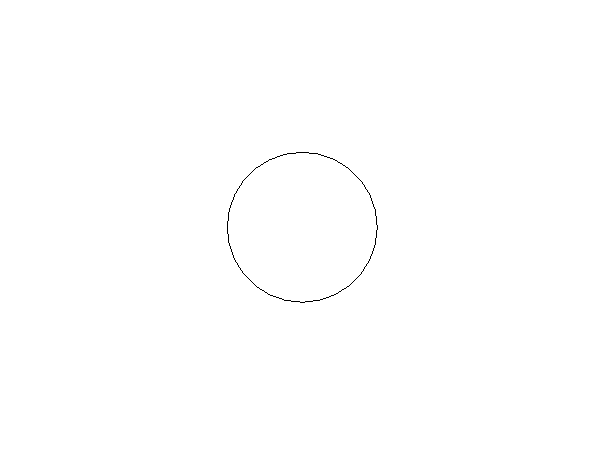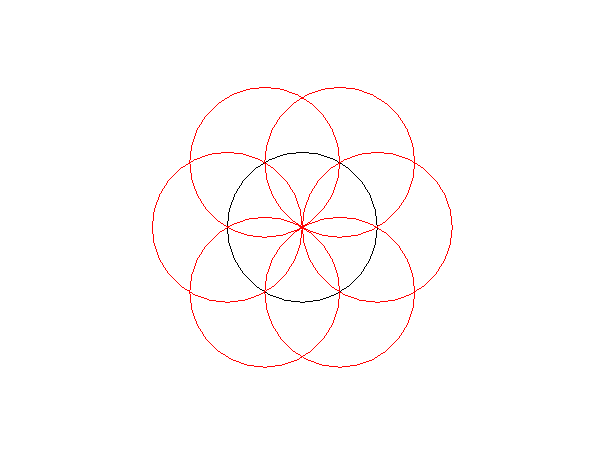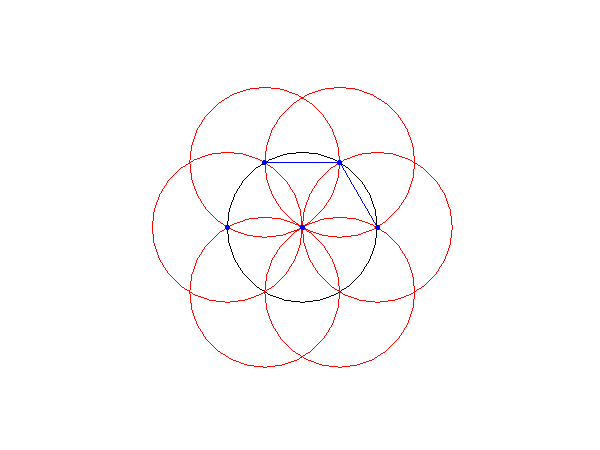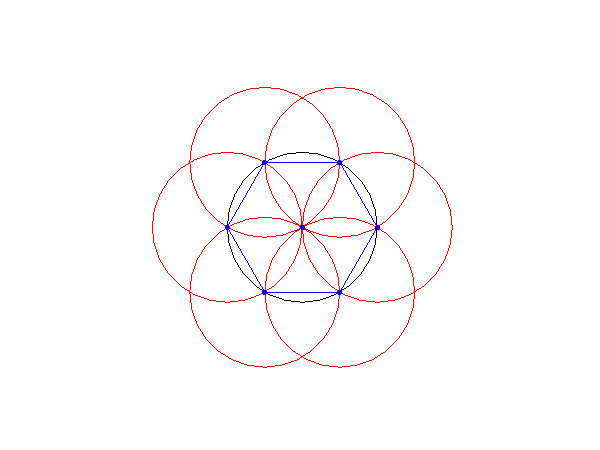
3.2. Hexagon construction
Input: a radius for the circle.
Step 1: Draw a circle with given radius.
Step 2: From the left side of the circle draw another circle.
Step 3: Form where these 2 circles intersect, draw another circle.
Step 4: Repeat in an anitclockwise direction until 6 circles have been drawn over the original circle.
Step 5: Mark teh intersection points and connect them.
1import turtle
2import io
3from PIL import Image
4from pathlib import Path
5
6
7def draw_centered_circle(t, centre=(0, 0), radius=10, penw=1, penc="black", fillc=None):
8 t.pu()
9 t.goto(centre)
10 t.seth(0)
11 t.fd(radius)
12 t.seth(90)
13 t.pensize(penw)
14 t.pencolor(penc)
15 t.pd()
16 if fillc is not None:
17 t.fillcolor(fillc)
18 t.begin_fill()
19 t.circle(radius)
20 t.seth(0)
21 if fillc is not None:
22 t.end_fill()
23
24
25def draw_circles(t, center, num_circles, radius, images):
26 # do central circle
27 draw_centered_circle(t, centre=center, radius=radius, penw=1, penc="black")
28 # Capture the screen and add to images
29 screen_img = turtle.getcanvas().postscript(colormode="color")
30 img = Image.open(io.BytesIO(screen_img.encode("utf-8")))
31 images.append(img)
32 # surrounding overlapping circles
33 angle_increment = 360 / num_circles
34 for i in range(num_circles):
35 t.pu()
36 t.goto(center)
37 t.seth(angle_increment * i)
38 t.fd(radius)
39 circ_center = t.pos()
40 draw_centered_circle(t, centre=circ_center, radius=radius, penw=1, penc="red")
41
42 # Capture the screen and add to images
43 screen_img = turtle.getcanvas().postscript(colormode="color")
44 img = Image.open(io.BytesIO(screen_img.encode("utf-8")))
45 images.append(img)
46
47
48def draw_hexagon(t, center, num_circles, radius, dot_size, images):
49 # Draw dots at hexagon vertices
50 t.penup()
51 t.goto(center[0], center[1])
52 t.pencolor("blue")
53 draw_dot(t, t.pos(), dot_size)
54 # Capture the screen and add to images
55 screen_img = turtle.getcanvas().postscript(colormode="color")
56 img = Image.open(io.BytesIO(screen_img.encode("utf-8")))
57 images.append(img)
58
59 # t.setheading(0)
60 # t.penup()
61 # t.forward(radius)
62 # draw_dot(t, t.pos(), 15)
63 # t.setheading(120)
64 angle_increment = 360 / num_circles
65
66 t.pu()
67 t.goto(center)
68 t.seth(0)
69 t.fd(radius)
70
71 draw_dot(t, t.pos(), dot_size)
72 # Capture the screen and add to images
73 screen_img = turtle.getcanvas().postscript(colormode="color")
74 img = Image.open(io.BytesIO(screen_img.encode("utf-8")))
75 images.append(img)
76
77 for i in range(6):
78 t.pu()
79 t.goto(center)
80 t.seth(angle_increment * (i + 1))
81 t.fd(radius)
82
83 draw_dot(t, t.pos(), dot_size)
84 # Capture the screen and add to images
85 screen_img = turtle.getcanvas().postscript(colormode="color")
86 img = Image.open(io.BytesIO(screen_img.encode("utf-8")))
87 images.append(img)
88
89 t.left(240)
90 t.fd(radius)
91 # Capture the screen and add to images
92 screen_img = turtle.getcanvas().postscript(colormode="color")
93 img = Image.open(io.BytesIO(screen_img.encode("utf-8")))
94 images.append(img)
95
96
97def draw_dot(t, position, size):
98 t.penup()
99 t.goto(position)
100 t.pendown()
101 t.dot(size, "blue")
102
103
104def main():
105 SCREEN_WIDTH = 800
106 SCREEN_HEIGHT = 600
107 CIRCLE_RADIUS = 100
108 NUM_CIRCLES = 6
109 DOT_SIZE = 5 # 5mm dot size
110
111 s = turtle.Screen()
112 s.bgcolor("white")
113 s.title("Hexagon Construction using Compass")
114 s.setup(width=SCREEN_WIDTH, height=SCREEN_HEIGHT)
115 s.tracer(1, 1)
116
117 t = turtle.Turtle()
118 t.speed(0)
119
120 center = (0, 0)
121 images = []
122
123 t.hideturtle()
124
125 draw_circles(t, center, NUM_CIRCLES, CIRCLE_RADIUS, images)
126
127 draw_hexagon(t, center, NUM_CIRCLES, CIRCLE_RADIUS, DOT_SIZE, images)
128
129 draw_dot(t, center, DOT_SIZE)
130 screen_img = s.getcanvas().postscript(colormode="color")
131 img = Image.open(io.BytesIO(screen_img.encode("utf-8")))
132 images.append(img)
133
134 currfile_dir = Path(__file__).parent.parent
135 gif_path = currfile_dir / "gifs" / "hexagon_construction.gif"
136
137 images[0].save(gif_path, save_all=True, append_images=images[1:], duration=500, loop=0, dpi=300)
138
139 s.update()
140 s.exitonclick()
141
142
143if __name__ == "__main__":
144 main()